Introducing Continuous Data Protection (CDP) as a viable back-up strategy
You thought back-ups only happens on a scheduled basis (once in a day, etc)? Ever saved a wrong entry in excel sheet and wondered how to go back to the previously saved version? Been on continuous travel without access to corporate back-up mechanisms and the hard disk crashes right then? Well, there is something you ought to know then – Continuous Data Protection. Read on…
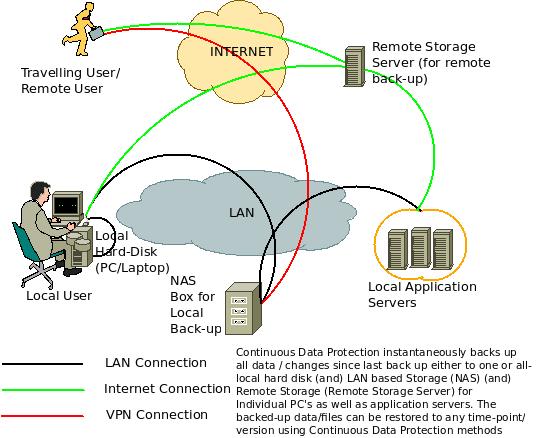
What is Continuous Data Protection (CDP)?
The concept of Continuous Data Protection (CDP) can be best summed up by the above diagram. There is a local user (within LAN) who works with a lot of files. With a normal scheduled back-up, all the files get backed up only during a certain time period (Lunch Time or after office hours – each day or each week). But with Continuous Data Protection (CDP), the files get backed up immediately after this user clicks the ‘Save’ button. Suppose the user makes a mistake and wants to have the previously saved version of the file, it is possible to recover it with CDP. Even if the user has saved the same file ten times with different modifications, he can access any of the ten versions of the file as all of them will be backed up.
The local user can save the back-ups in his own PC/ Laptop (Hard Disk) (OR) a NAS (Network Attached Storage) box in the LAN (OR) a remote storage server via the Internet (OR) all of them at the same time.
The same can be done for servers and their applications. For remote users/ traveling users, the back up happens via a VPN connection to the NAS box (OR) in the remote storage server via the Internet. Even if they are not connected to any network, the back up is automatically queued in their own hard disk and pushed when a connection is established.
Whatever be the case, continuous data protection ensures that critical data is always back-ed up (preferably in multiple places) immediately after the user hits the ‘Save’ button.
Advantages of Continuous Data Protection (CDP):
- The back-up happens instantaneously once the user hits the ‘Save’ button – So, the most recent (and the most important) data will be safe.
- In the event of viruses or disk corruption, even if all the files in the PC/ Laptop becomes inaccessible, there is a back-up of all those files waiting to be restored immediately.
- Back-ups can go to one or more disk targets (either locally in the LAN) or in a remote location (via Internet).
- The backed up copies of the files can be in their native formats (except for compressed or encrypted files) which can be accessed in the same way that normal files are accessed in a storage device.
- Version Control is possible, meaning, even if the same file is saved ten times with ten different modifications, any of the files can be recovered at any time by the user itself, without the intervention of the system administrator.
- Continuous Data Protection methods uses disk based storage (against tape drives, etc) and the cost of the disks for storage is coming down rapidly while at the same time, their capacities are increasing rapidly too.
- Even remote users/ traveling users can use CDP for backing up their data. If no connection is available, the back up is queued in the local hard disks and is pushed to the storage devices once a network becomes available keeping the version control intact.
- Scheduled back-up methods create bursty traffic in the LAN/ WAN as all the files are being backed up at the same time. This may reduce the network performance for other activities during that time. But with CDP, as the files are backed up instantly, the back up process happens at different periods of time (distributed) and hence there is no major burst in the data traffic.
- Some CDP solutions have a feature called Vault which allows certain files to be protected (from being deleted or modified) for a specified period of time by anyone accessing it.
- Continuous Data Protection can happen along with a Scheduled Back up (CDP can be used for top level executives and frequently updated servers while all other data can be backed up on a scheduled basis).
- Files stored on the remote location can be encrypted (to protect them in case of multiple users accessing the server) or compressed (in order to save storage space)
- For large files, CDP has an option of storing only the changes at the remote location for each incremental version instead of storing the entire files in order to save bandwidth. But the server processing resources used in this case is more.
- There is also another option called bandwidth throttling which enables the maximum rate of transfer of the files to be backed up from the local user to the NAS box or remote storage server so that big files do not congest the network bandwidth being used for other purposes.
- Certain CDP solutions allow defining of back-up policies wherein the users can select the type of files that can be included and excluded in the back up process (all xls files need to be included and all mp3 files need to be excluded, for example).
- Some CDP solutions even send an email alert once the storage disk is nearing its full capacity (if more space is not created, then the oldest back-up files will be over written first).
- Some CDP solutions allow data to be backed up on a USB based flash drives/ external hard disks.
- Backed up files can be selected for restoration using multiple parameters (like file name search, search by application, version, size, location, etc).
- Some CDP solutions are tailor made to suit specific applications (CDP for MS-SQL database back up, for example).
Types of Continuous Data Protection (CDP) Solutions:
Basically there are two types of CDP solutions – CDP and Near CDP (The Near CDP type of solution takes continuous back-ups in frequent intervals (like one hour, for example) and restoring to any of those periods instead of backing up instantly like their CDP counterparts.
Continuous Data Protection solutions can be appliance based or Software based. Most of them offer a software client (with easily usable GUI interface) to be loaded on the PC/ Laptop whose files need to be backed up.
CDP solutions can be block based or file based – Block based solutions operate at block level of logical devices which means that the back up is taken on secondary storage disks as and when data blocks are written to the primary storage disks and that too on individual block level. The main advantage of this is that it works across any data type. This is more suitable for servers. File based CDP solutions operate at physical file level. There are limitations on the types of files (based on applications) that can be backed up by this type of CDP. This is more suitable for individual PC’s and Laptops.
excITingIP.com
In case you may have any additional points to add on this topic, you can do so in the comments section given below. In case you have any questions or want to contact us, you could use the contact-form for the same. You could also stay up to date on the various topics and concepts in the networking industry by subscribing with your email address in the box titled “Get Email updates when new articles are published”.