Different ways to do a Video Conference – Personal and Professional
There are so many situations when we wish we could see and talk to another person/ few people – both for personal and professional reasons. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which we can do that as long as there is some form of connectivity between the two people wanting to see and talk to each other. So, we will look at the various ways to do an effective video conference – both from personal and professional point of view and the infrastructure/ connectivity required for the same.
Personal Video Conferencing:
Video Chatting: Many services like Gtalk, Skype and even professional alternatives to the same allow to do a video chatting between two people connected over the internet/ intranet. This is the most common and least expensive form of ‘seeing and talking’ to each other, but the quality in most of the cases suffer. There is also some delay in the transmitted images at the far end which makes the visual movements etc. look slower and broken sometimes.
Required Infrastructure: PC, Webcam, Headset/Mic (or) speakers/mic, broadband/leased line internet connectivity and a messenger software like Gtalk, Skype etc.
Pros: Cheap, Available anywhere, IM service is free of cost, Uses the internet which is commonly available.
Cons: Average Picture quality (as most webcams come with a lower resolution) and delayed reception/display of images.
Before we move on, we need to know about an important video compression format called H.264. Also called MPEG 4 Part-10, H.264 is a compression technology used by video transmission/ storage systems to give a good compression ratio for transmitted/ stored videos. Since it is a standard, any manufacturers device at one end can compress and send the video files and the same can be de-compressed by another manufacturers device at the other end. The advantage of H.264 is the achievement of better video quality at a lower bandwidth (when compared to uncompressed video). Do look for this H.264 compression format enabled devices if you choose any of the below video conferencing devices – it really helps and is crucial for a good quality video conference especially over the internet.
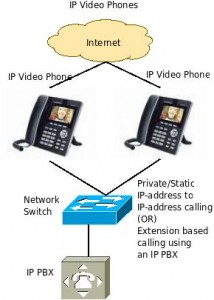
IP Video Phones:
IP Video phones are not very popular, but offer a good and an effective choice for personal video calling between two persons, sometimes even three. Interestingly, the video phones use open standard VOIP protocol called SIP. That makes it easier for them to integrate in to business VOIP System as an IP extension and hence can receive voice only calls as well as video calls. Some video phone manufacturers also offer an unique phone number that can be used anywhere (over the internet) to call another phone of the same manufacturer/ model. That makes it easier than having to procure a static IP address at each end or having to register them with an IP PBX. Interestingly, you can also call from an IP Video Phone to any standard Professional Video conferencing system if the latter supports video over SIP (or) IP-SIP protocol. And yes, some of the video phones support H.264. Click here to go through a detailed feature list supported by IP Video Phones.
Required Infrastructure: IP Video Phones (at both ends) and internet connectivity (preferably an Internet leased line/ high speed broadband) as at least 128 Kbps upload and download is required for a single channel of video to be transmitted at 15 frames/ second. Some manufacturers of the IP video phones include Polycom, Grandstream etc.
Pros: Can work independently or with an IP PBX, can be used with video conferencing systems that support SIP, relatively cost effective, can work with broadband as well, supports H.264.
Cons: The interoperability between IP Video phones of different manufacturers is not widely tested, smaller screen, limited audio (over speaker phone/ handset), average quality of images over broadband connections operating at lower speeds.
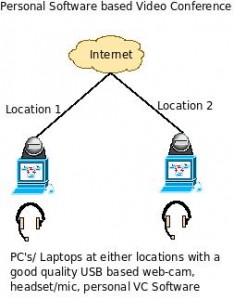
Software/PC based Personal Video Conferencing Systems:
As an interesting alternative to video chatting, there are certain software’s that are provided by professional video conference system manufacturers that can be downloaded to any standard PC (at both ends) and can be used along with any standard web-cams and headset/mic or speakers/mic. The crucial thing that the provided software does in addition to giving a user interface is that it can do H.264 compression/ decompression of the video using the PC hardware/processor which gives excellent quality of images even at lower bit rates. You can also call a professional video conference system from the PC equipped with the personal VC software edition. Click here for a detailed description of PC based Video Conference systems.
Required Infrastructure: PC/ Laptop, Internet (high speed broadband/ internet leased line at least 128 Kbps dedicated – upstream and downstream), good quality standard web-cam and microphone/headset. Some examples of such systems include Polycom PVX, Tandberg Movi, Radvision Scopia etc.
Pros: Lower cost, higher quality, uses standard PC/webcam/headsets etc, supports H.264, High Definition Formats (HD).
Cons: The video quality depends upon the web-cam quality, all of which may not be very good. Lack of external microphone means wearing the headset continuously. The in-built microphones of PC/Laptop may not provide good audio quality.
Depending on the manufacturer, some of them also offer hardware based personal video conferencing systems that range from personal VC codec/camera to personal LCD monitor with integrated camera/mic/speakers.
Professional Video Conferencing:
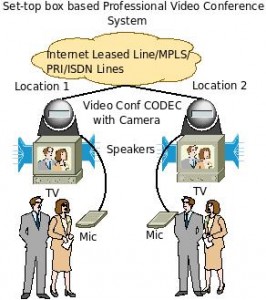
Professional Video Conferencing Systems (Set-Top Boxes):
These systems are more for companies/ organizations which have a requirement of one or few people from one place to see and talk to one person/few people at another place. Normally, a set-top Codec is supplied by the Video Conference vendors which connect to monitors/ projectors/ plasma etc for display, microphones (mostly supplied by the manufacturer of the video conferencing systems), ISDN/PRI(E1/T1) Lines OR Internet Leased Lines. Most of these set top boxes support H.264 and require at least 128 Kbps of Internet Leased Line (Or intranet bandwidth) to work fine. Some of them even support HD formats for superior video quality but require higher bandwidth. You can also use document cameras/ dvd players to display objects/ videos to the other end. Most of them support dual video output streams for displaying video along with data (power point presentations etc) for better collaboration. Such systems support one person at either end or many people, depending on the model of the video conference system. Some of them even allow for viewing people from multiple locations simultaneously (normally 1+3/4, and can be expanded to accommodate many sites using a multi-conference system). Click here to know more about High Definition Video Conference systems and click here to know more about multi-site video conference systems. The below block diagram for professional VC systems should be self-explanatory.
Requirements: Video Conference system (usually codec), microphone(s), monitor (TV, projector, LCD display, plasma etc), speakers, bandwidth (Internet leased lines/ MPLS/ LAN). Some manufacturers who supply such systems include Polycom, Tandberg, LifeSize, Aethra, Sony etc.
Pros: Can accommodate single to multiple persons at each side, cameras support pan/tilt/zoom/preset functions, can display data (presentations) along with video, supports H.264/HD formats.
Cons: Higher cost and higher bandwidth requirements.
Tele-Presence:
A video conference system cannot get better than Tele-Presence (at least for now). This is the ultimate in video conferencing where the users are made to feel as if the other person is sitting and talking to them from across the table, in real time. A lot of preparation goes in to such systems for giving such an experience – right from the table size, colour, shape, monitor and camera locations, lighting arrangements, display of life-size images, bandwidth etc. at both the locations. Some manufacturers also let individual Video Conference systems to inter-operate with their Tele-Presence systems. Click here to get a better idea of the components involved and requirements for Tele-Presence systems.
Click on the following Youtube link to see a demonstration of Tele-Presence system : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0kd2SO1_kSA
Requirements: Click here. Some manufacturers include Polycom, Tandberg, Cisco etc.
Pros: Real-time and life-like meeting experience.
Cons: Very high cost and very high bandwidth requirements.
excITingIP.com
In case you want to add something to the topic or have any clarification on the same, please feel free to leave a comment below or contact us using the contact form. You could also subscribe with your email address in the box that says “Get email updates when new articles are published” to get updates when new articles are published on this website.
Video conferencing is a great technology helping businesses and people in reduced travel costs, better client interaction, increased productivity etc. Tools like R-HUB desktop video conferenciong servers, webex, gomeetnow, gotomeeting etc. are widely used by businesses for conducting online video conferences.