Telecom Trunk Lines – Difference between Analog line, PRI/E1/T1 Digital Line & GSM Gateway
In this post, we will see a short overview of the various trunk lines available for connecting your PBX to the external world. We will have a look at analog lines, PRI/E1/T1 Digital lines & GSM Gateway, in particular. This topic was requested by a reader in the comments section and hence I am writing an article on this topic. If you want to know more about any topic, leave a comment in this blog and I will try to write elaborately on the same.
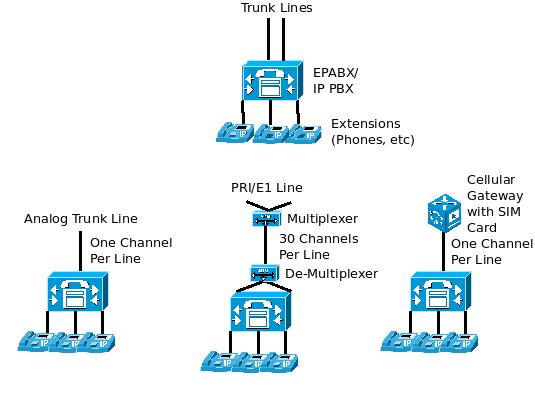 Why do you need a PBX?
Why do you need a PBX?
Before we go into the actual post, we need to understand some background about what is a PBX and why we need it. PBX actually refers to Private Branch Exchange. Imagine this situation – You have 100 employees in your organization, and all of them work from their office. Each one of them need to make outgoing calls (to partners, customers, etc) and also need to talk to their colleagues.
If there was no PBX, you have to procure 100 different analog trunk lines (from a Telecom service provider) to give telephone access to all of them. They can call each other, but those calls will also be charged as they are routed from the public telephone exchange. So, obviously this method is inefficient.
So, a small private branch exchange – PBX (Telecom switch) is kept at the organization to achieve two important purposes :
1. To share the incoming (trunk) lines from public telephone exchange to all employees as every employee is not going to be making outgoing calls/ receiving incoming calls all the time. So, instead of buying a trunk line for every employee, you might just buy one line for ten employees (sufficient in most cases) and share them.
2. To make internal calls (based on extension numbers) without any charge. Since the PBX is a mini-switch, it can route calls from one extension to another extension internally.
Analog Trunk Lines:
The phone line (land-line) that you get in your home is an example for an analog trunk line. At homes, one line would suffice. But in organizations, multiple such lines might be required (as the number of telephone users are more). These analog trunk lines carry a single channel of voice call per line (meaning, one person can make or receive a phone call from outside at any given point of time).
For terminating the analog trunk lines in a PBX, special analog trunk cards (12 ports, 24 ports, etc) are used. In an IP PBX, Analog Terminal Adapters (ATA) or PCI based Analog Cards may be used. These devices convert the analog calls into IP so that an IP PBX can understand them and transmit them over the network.
Separate rental / call charges needs to be paid for each analog trunk. Analog trunk lines are sufficient for small organizations which require a few lines.
PRI / E1 / T1 Lines:
For larger organizations that require a lot of trunk lines, procuring additional analog trunks might not be a practical idea as they need to buy separate (perhaps multiple) analog trunk cards to terminate these lines in their PBX (and) they need to pay separate rental for each line where the free call capacity for some individual lines might never be reached!
So, these organizations can procure a digital line called as PRI/ E1 (In Europe/ Asia) or T1 (In America). Each PRI / E1 line can carry up to 30 channels of voice communications simultaneously. They can do this by using multiplexing/ de-multiplexing techniques (at the public telephone exchange end -and- the customer PBX end). A T1 line, similarly can carry up to 24 channels of voice communications simultaneously.
At the customer end, they need to procure a PRI / E1/ T1 Card, to terminate this PRI/ E1/ T1 line in their PBX. Just imagine – One line coming into your organization but thirty people can simultaneously make or receive calls through it! And add to it a single consolidated rental / billing package from the Telecom company. You can read more about PRI lines and its advantages from here.
There is another type of digital line called ISDN line. With ISDN, two simultaneous calls can be made/ received at the same time using a single line.
GSM/ Cellular Gateway:
In some situations, it may not be feasible to lay analog lines (over a hill, rural areas, etc). But those places might be covered by cellular companies/ signal from cell phone towers. In such situations, you can use a GSM / CDMA Cellular gateway device called as Fixed Cellular Terminal and use the Cell phone SIM cards as analog trunks for your PBX. These devices are in fact connected to the analog trunk ports of the PBX.
A Fixed Cellular Terminal is a small device in which you can insert a SIM card and connect the single-pair copper telephone cable coming out of it, directly to a telephone (or) to a PBX. At the other end of the PBX, the extensions (normal phones) are connected. So, when someone makes an outgoing call, the request reaches the PBX and the call is directed to the Cellular Gateway which has the SIM card. Some cellular gateways have multiple SIM cards, enable multiple simultaneous calls to/from outside.
So, even though people might dial a number from their land line extension, the call actually goes through the cellular network using the GSM/ CDMA Cellular Gateway.
VOIP / SIP Trunks:
Of late, VOIP service providers have become very popular. They use the Internet backbone (mostly) to transmit the call as IP packets to the destination. They have gateways (where required) to convert the IP calls to analog calls before passing them on to the local telephone exchanges so that people can reach normal landline/ cell phone numbers using the VOIP Service. You can read more about SIP Trunks from here.
excITingIP.com
You could stay up to date on various computer networking/ related IT technologies by subscribing to this blog with your email address in the sidebar box that says, ‘Get email updates when new articles are published’
Also i would request you to provide us the difference B/w PRI and BRI
The basic difference is that, while a PRI Line carries 30 Channels on a single circuit (one can make 30 simultaneous calls using it), a BRI Line carries 2 Channels on a single circuit. Both are digital lines. You can refer to the following articles to understand further about either of them.
https://excitingip.com/687/what-is-a-pri-line-what-are-the-advantages-and-limitations-of-pri-circuits/
https://excitingip.com/834/applications-of-isdn/
Thank you sir, Nice infomation about Trunks.
Many thanks, make me more understanding.
it was great, it is beautifully explained with practical scenario
Very good explanation…..thanks
Very Nicely Explained.
We have a trunk line system in our office, however we would like to add several handheld phones we could walk around with that would function same as our multi-line desk phones do. We would probably use 5-10 additional handheld units.
Thanks,
Ben
thanks guys it has helped me alot
Hi,
Great post and very clear.
Can you please post about Calling search space ,Partition, call routing,
routelist
Thanks
Aravindan
Can some one tell me about how many toll free numbers can be mapped in a single PRI line
1 DID number can be used to make 23 calls in T1 ckt
Many Thanks
Thanks, your explanation really helped. Could you explain PRI over DOCSIS how is it different and its advantages? Many thanks
I am starting a WISP business here in the US, what is the process if I want to offer my customers T1?
Thanks
can you please explain how E1 works for both voice and data.
thenks alot.it was very useful.
Distinguish between Line and Trunk Signaling. Describe the process a telephone system hacker
would use to obtain free long-distance service using old in-band signaling telephone network. Why
is the out-band signaling such as SS7 network faster than the old in-band signaling method?
Thanksss a lot it was very helpful….!!!
I have a situation where the cable company is bringing in a PRI on their Fiber and expecting to connect to a PRI card in the Key System(KSU). The KSU is not PRI compatible, Is there a device that stands alone that will break out the chanels from the cable Co PRI to analoge for impute into the KSU and separate FAX and Credit card machine lines?
No
Very useful post.In the morning while studying the document of my company. Compnay’s data center shifting from PRI to VoIP. I just wanted to know that how PRI carries the voice ?
Still, keep PRI as secondary carrier and VoIP as Primary
gud article very useful
Can you make SIM card work is a e1 line
Excellent!!! Nice info.Many thanks to you sir.
Good article
sir,
it’s nice and i need information on this also
please tell me how the data and voice connection is possible with practical example
Good Artile
Hi ,
Your Explanation is Excellent am very much Impressed
Can you pls Explain about RNC’s & EVORNC’s and MGWs and Blade Clusters
I mean the Overview
Rgds,
naren
9000400302
well explained….. from where i can get more topics for telecommunication ?
very good explanation….very use full…
thanks… It was great reading your explanation on “Difference between Analog line, PRI/E1/T1 Digital Line & GSM Gateway`.
Which course I should do to have the Basics on Telecommunication ?
GOOD EXPLANATION THANX A LOT……..!!
Thank You…very much. It was really great differentiation of trunks. Can you please elaborate the same with example..?
Hi.
I would like to start a service that will require several simultaneous calls in & out.
The Pri lines are not an option.
I thought of a GSM gateway but was faced with an issue. The service should have a single number that customers call and from what i found out the GSM technology does not support number pooling grouping.
So what options do I have what do you suggest? can an analog land line plugged into a dialogic with asterix behind accomplish this ?
your help is greatly appreciated.
Salem
You ROCK Rajesh!!
Could you also explain something about VoIP trunks/SIP ?
Much appreciated
That was really helpful. Thanks a bunch.
Excellent
Its very use full and great post
Many thanks!
Thank you. This was very helpful.
Good Explaination …
Very informative!
Please Notify Me On Your Technological Advancement,otherwise Am A Ugandan Who Would Love To Specializing In Telecommunication Technology.
As a new telecom technician i found this information very important and enlightening as i work with this technologies in the field and would like to get more as to become the best in what i do
Is it legal to use Sim-By-Pass on PRI lines for National calls (Fixed – to – mobile)??? That is, when a FL customers dials another FL number, the call is routed using sim-by-pass and looks like a mobil – to – FL call.
Very good
Hi,
Great post!
I’m still familiarizing networking and this article really did me a favor. It deepened my knowledge about telecommunications. Thanks for posting this article. It really helped me.
Regards,
Rio
good tips, but i will like to know how to map each of the 30 PRI lines to each extension on my pbx for both incoming and outgoing calls.It has been my headache for months now
On the pbx equipment how to identify analog,digital and ip ports?
HI,
I wanted to know that can normal gsm postpaid sim can be change in PRI number