What is FTTH – Fiber To The Home & Advantages of P2P vs P2M/PON Architectures
Enterprise Fiber Networks seem to get the raw deal these days! Fiber To The Home (FTTH) can get Fiber Cable up to the Desk of a person accessing Internet at home & they can send and receive signals on the same fiber strand! Let us take a closer look at the two popular architectures that seek to dominate the FTTH market – P2P (Point to Point) & P2M / PON (Point to Multi-point), along with some advantages of each.
What is FTTH (Fiber To The Home)?
If you are still using copper DSL lines to access broadband Internet at your home, you’re so much from the past! Fiber to the Home is the next big thing according to FTTH vendors and service providers who have bet big on this technology.
Need for Speed, seems to be the priority of the day and with steep competition from 3.9/4G Technologies & even Satellite technologies that are racing ahead for providing faster broadband, the terrestrial broadband providers have responded with FTTH – Fiber To The Home. At times, even to your desk!
How much bandwidth can your broadband technology give you? 1 MB? 5 MB? 10 MB? FTTH technologies can give a minimum of 100 Mbps per house, if Point to Point technologies are used. Heck, they can even go up to 1 Gbps or 2.5 Gbps per house with currently available technology. 1 Gbps of bandwidth connectivity to home? Whatever are you going to do with so much speed? Well, that’s a small unwanted detail and is usually left to the subscriber to ponder upon 😉
Some applications that might be sent to your home via Fiber cables include High Speed Internet, Cable TV, On-Demand IPTV, HD Content, Movie Streaming, Telephone System, Multi player Gaming, Video Conferencing, 3D, Virtual Reality, and what not!
Obviously, this technology requires service providers to lay fiber cables at all those places where existing copper telephone lines run today.
FTTH Architectures – P2P & P2M/PON:
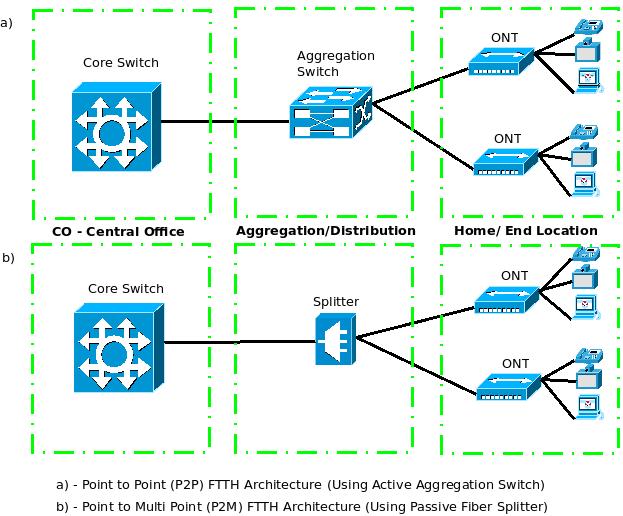
There are two popular architectures used with FTTH – The Point to Point (P2P) Connectivity Architecture which uses all Active Components throughout the chain & Point to Multi-Point (P2M)/ Passive Optical Network (PON) Connectivity Architecture which uses Passive Optical Splitters at the aggregation layer, as shown in the below diagram.
If you look closely at the above diagram, both the architectures are similar on the Central Office (CO) side and the Residential Complex side. They differ only in the Aggregation points (in the middle).
The Point to Point (P2P) architecture has a Core Switch at the Central Office which connects over Optical Fiber Cables to an Aggregation Switch at the Distribution Points. These locations are typically your street corners, etc. The aggregation switches have many fiber ports and each port will directly connect to an ONT (Optical Network Termination points) placed at the residential localities using fiber cables. Typically, just outside your home or even inside it, in some cases. From here, subscribers can use any access technology like Cat x cables/ wireless access points to complete the connection to their PC’s, and other devices.
The Point to Multi-point (P2M)/ Passive Optical Network (PON) architecture is the same, except in the distribution points. Instead of the Active Switches with Fiber Ports, Passive Splitters are used. These splitters do not require any power supply and they can divide an optical signal into 32, 64 or even 128 shared connections. The same signal is transmitted to all the houses beyond the splitter, but each ONT’s in each house knows how to decipher the information meant only for itself. Of course, the ONT’s used in P2P are different from the ones used in P2M. Also, the total bandwidth is shared between all these shared connections. There are different types of PON like GPON used more in America, EPON used more in Asia, etc but that is out of the scope of this article.
Advantages of P2P Technology for FTTH:
1. The bandwidth in each port of the aggregation switch is dedicated to individual homes and there is no sharing of bandwidth. So, higher bandwidth per port (and hence per home) can be achieved through this technology.
2. This technology provides symmetrical bandwidth (equal bandwidth for upstream/ downstream) which is critical for some applications like HD Video Conferencing, Peer-to-Peer file sharing, etc.
3. P2P Technology is a standard technology and the bandwidth can be limited/ controlled per port and hence each house can have a bandwidth plan tailored to its requirements.
4. P2P technology can carry signals over a longer distance using fiber (100+ KM compared to 20+ KM for P2M). Trouble shooting faults is easier and can be done using OTDR- Optical Time Domain Reflectometer.
5. This technology is better for viewing Video On Demand/ Streaming video using multi-casting.
Advantages of P2M/PON Technology for FTTH:
1. Irrespective of all the propaganda all over the Internet, P2M technology is less expensive to implement and maintain. It uses less active ports to terminate fiber and uses lesser fiber cables.
2. The fiber splitters don’t require power supply and hence they can be placed anywhere on the field according to the project requirements. So, there is more installation flexibility.
2. With encryption, each connection can be secured/isolated to a good extent.
3. It gives higher downstream bandwidth, and lower upstream bandwidth similar to current broadband technologies. But both of them are sufficiently and considerably high (GPON, for example, can give up to 2.5 Gbps of downstream bandwidth & 1 Gbps of upstream bandwidth, but that is shared among 32/64 users).
4. One can use traditional / digital set-top boxes to see TV through fiber cables using PON technology as these signals can be carried on an additional wavelength. These set top boxes are less expensive to buy when compared to IP set-top boxes.
5. The passive splitters are more rugged and can be used even in industrial environments, unlike the air-conditioning comfort needed for fiber switches.
excITingIP.com
You could stay up to date on the various computer networking / enterprise IT technologies by subscribing to this blog with your email address on the sidebar box that says, ‘Get email updates when new articles are published’
What other advantages P2P network topology has?
The number 3. and 4. “advantage” of P2M/PON over P2P that you stated is false as P2P clearly beats P2M/PON in these additional two things. With P2M/PON it happens that the speed can not be as high as with P2P even if you are the only user who is connected to the passive splitter. Less range = less speed and higher diameter fiber core = less speed (comparing it to single mode cables).
So, there is a reason google fiber and other 1Gbps+ ISP’s are connecting it through P2P technology and not P2M/PON technology. think of it as VDSL2 vs Fiber Optics. P2P is future-proof when you look at the achievable speeds.
Google fibre is using GPON: http://networkmatter.com/2014/02/27/google-fibers-brewing-little-secret-exposed-its-gpon/